Composite fabric
Summary: It is a new type of material made of one or more layers of textile materials bonded by oil glue or hot melt glue.
Six internationally popular composite fabric techniques
1
Hot-sol powder dot coating composite fabric technology
2
Hot-sol slurry dot composite fabric technology ★ is PUR
3
Hot-sol powdered composite fabric technology
4
Hot-sol two-point composite fabric technology
5
Polyurethane spraying Composite fabric technology
6
Polyurethane roller-coated composite fabric technology★that is, PU
According to the number of layers Division:
Three layers: composite with film; second layer: composite without film
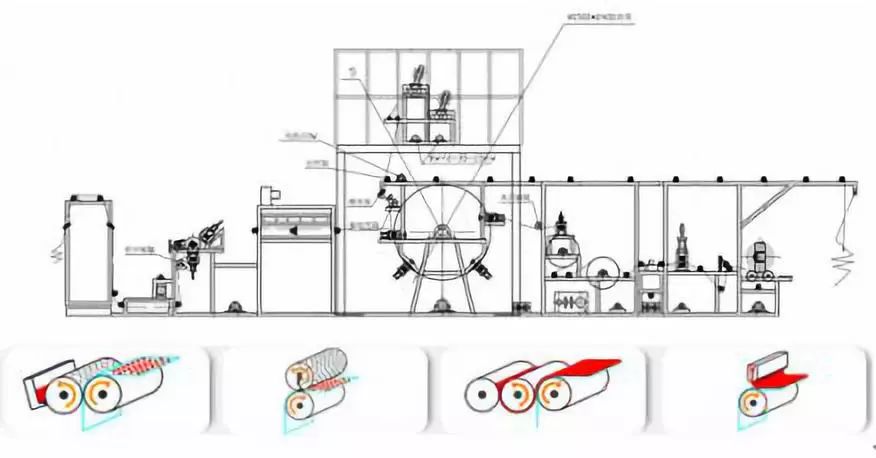
Production principle
The core components of composite equipment are the gluing device and the composite device. When the surface cloth (film) passes through the gluing device, it is squeezed by the gluing pressure roller. The glue in the glue eyes of the engraving roller is forced to transfer to the surface cloth (film), and then is pressed by the composite device to obtain the initial bonding. Fastness.
Production process
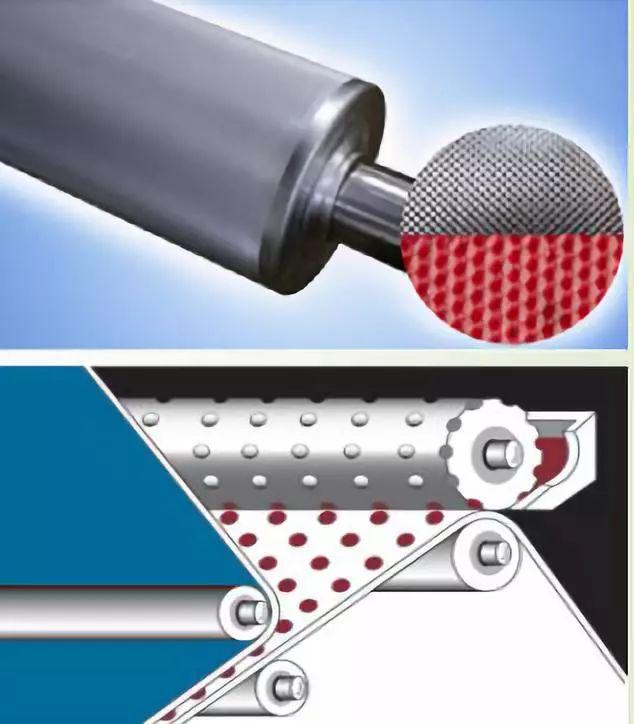

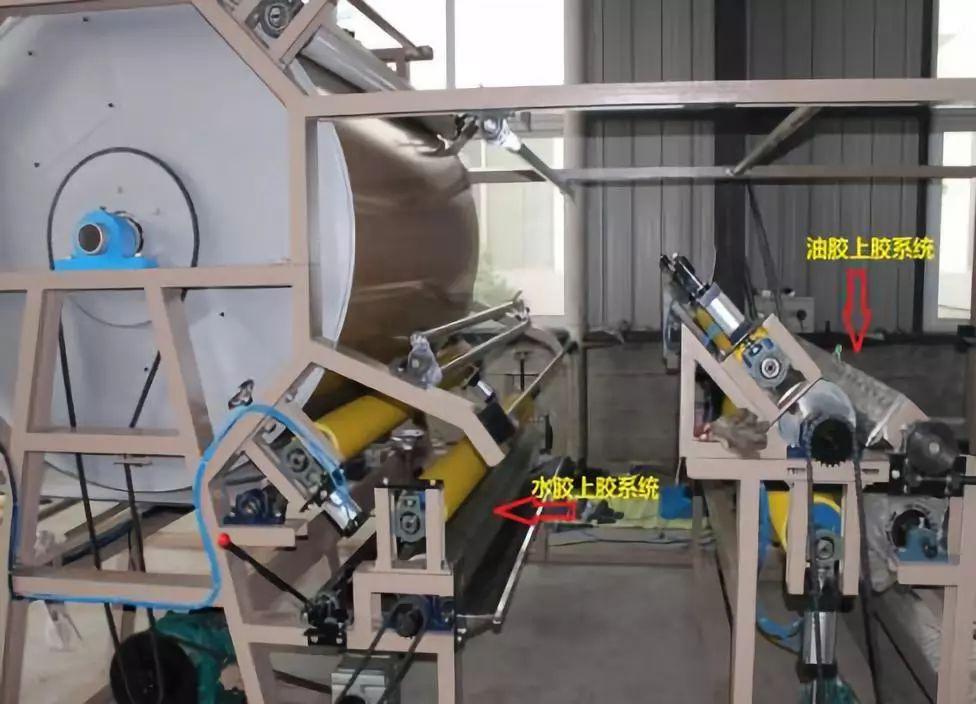

The gluing device
is an engraving roller and a gluing silicone pressure roller.
There are two general point shapes of engraving rollers: diamond points and round points.
The diamond-shaped points are arranged regularly, the points are consistent, and the water pressure resistance is relatively good. There are two types of circular dots: regular arrangement and irregular arrangement. The dot spacing is inconsistent and the water pressure resistance is relatively weak.
Maintenance treatment
The time of maintenance treatment has a great influence on the fastness of fabric bonding and The degree of fusion of the adhesive has a great influence. The maintenance and processing workshop is fully enclosed and a certain temperature and humidity are maintained indoors to allow the adhesive to fuse naturally. If the temperature is increased for quick completion, the yarn will be damaged during the sewing process of the fabric. It is easy to be broken by needles, feels hard, and makes a rustling sound when rubbing against each other, indicating that the adhesive has solidified on the fabric and hardened the yarn of the fabric.

PU process equipment
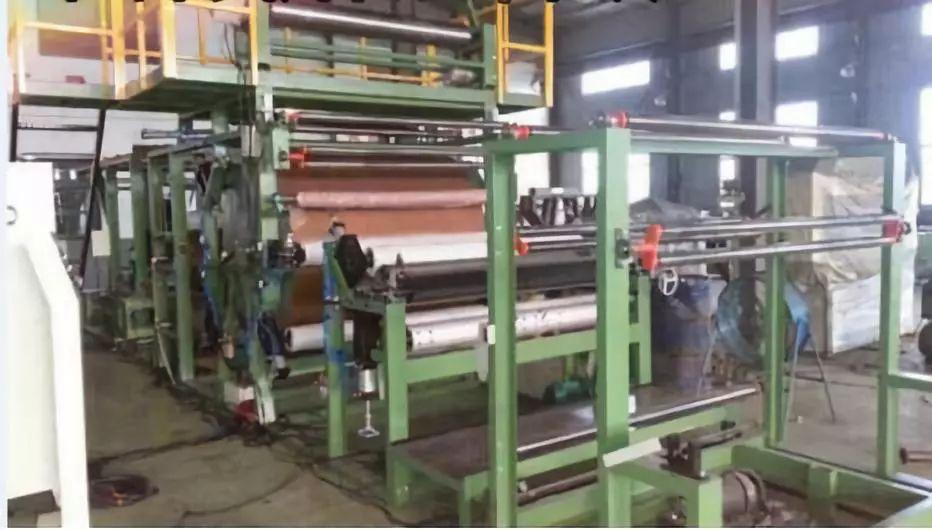

Traditional composite equipment, the original glue is heated and dissolved in In the solvent, the glue solution is manually added to the application tank, and the solvent is evaporated by hot pressure through the compound wheel.
The glue maturation conditions are 30℃×5day, so that the solvent can evaporate to the maximum extent.
Advantages and disadvantages of PU technology:
Advantages
1. Low cost, flexible and convenient operation
Disadvantages
1. The solvent is pungent and not environmentally friendly, and it is easy to produce APEO and formaldehyde
2. It is easy to mix impurities when applied manually, and the amount of glue applied to the glue points is unstable
3. If more glue is applied, the feel will be harder.
4. Ready-made garments cannot be dry cleaned
★This process has many problems. If it is not a chemical fiber fabric, it is recommended not to use this process
PUR process equipment
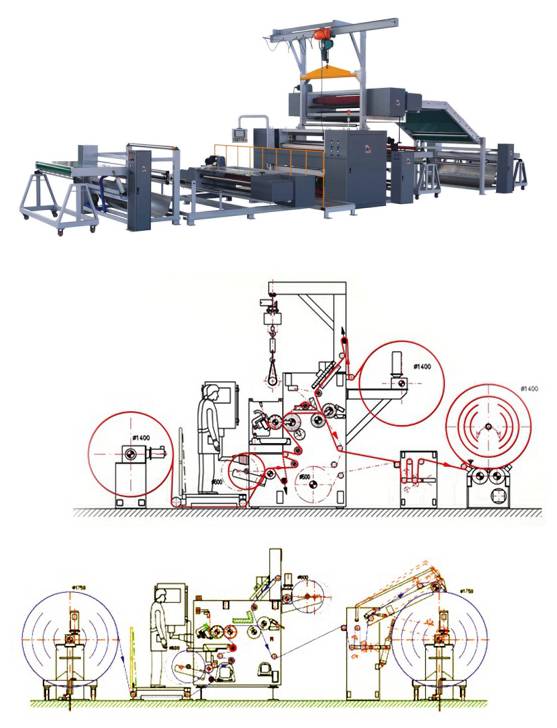
Uses 100% solid content single-component reactive hot melt adhesive, does not contain chemical solvents, is environmentally friendly and has no irritating smell. The machine applies automatically and the glue tank is heated.
The maturation conditions of hot melt adhesive are 30℃ room temperature, humidity >90%, and it must be left for 72 hours to achieve the final peeling effect.
Advantages and disadvantages of PUR process:
Advantages
1. Environmentally friendly, no odor, no formaldehyde
2. Reactive glue, long-lasting glue points, ready-made garments can be dry-cleaned.
3. The amount of glue is small and the hand feels soft
Disadvantages
1. The quality of glue is very important
2. The amount of glue is small and maintenance is difficult. If it is not sufficient, the peeling strength will be poor
Common problems with composite fabrics
1. Fabric color
1. The lamination process, gluing, hot pressing, drying and other processes have an impact on the color of the fabric.
2. If the top fabric is light-colored and the base fabric is dark, the color of the base fabric will have a greater impact on the color of the base fabric.
2. Washing off/foaming
After the fabric is compounded, it becomes sticky due to The bonding fastness is not good, and partial detachment or blistering occurs during washing.
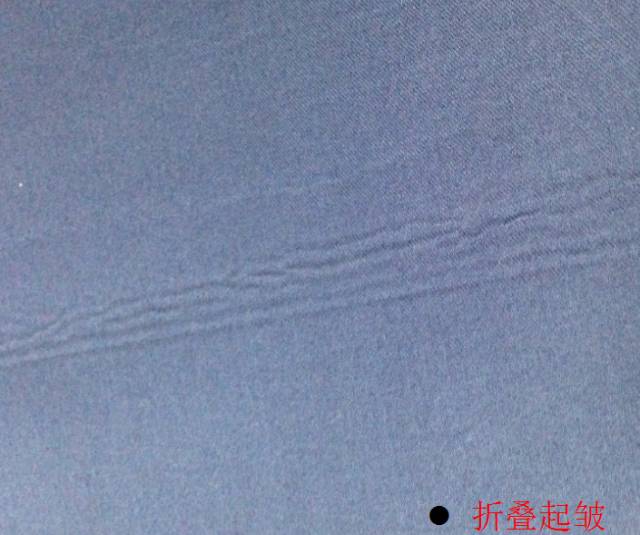
3. Fold and wrinkle
Non-elastic thin fabric is used as the top cloth and the bottom When the fabric is knitted thicker, it is easy to fold and wrinkle.

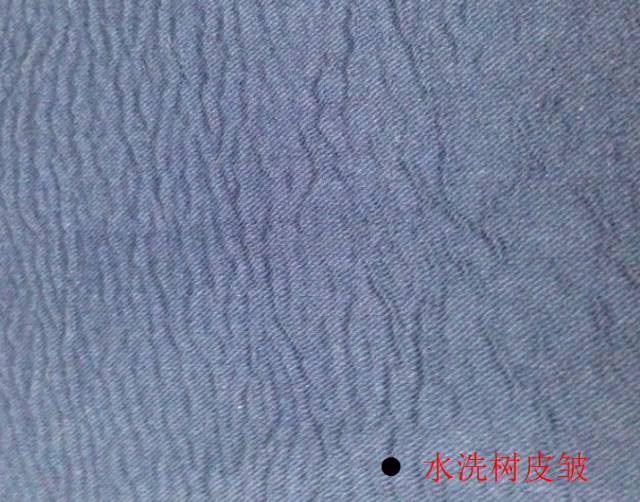
4. Washed bark wrinkles
Shrinkage of top and bottom fabrics When composite fabrics with a difference of more than 3 points and a large difference in fabric thickness are washed, bark wrinkles will appear on the thin fabric surface due to shrinkage differences.

5. Adhesive penetration
Woven fabrics are light-colored and thin. After the glue is matured, glue spots can be seen on the cloth surface.
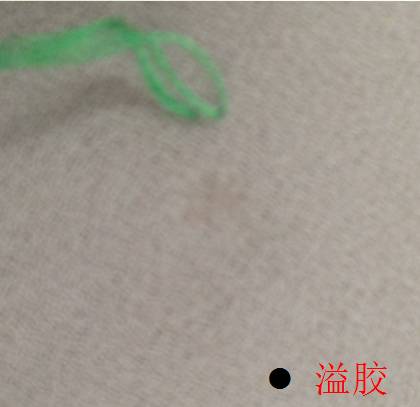
6. Glue overflow
A fabric with sparse texture and hard feel , it is easy for glue to seep out of the cloth surface.

7. The colored yarns of light-colored fabrics are highlighted due to compounding
White fabrics, especially It is a white woolen material. After lamination, due to the background of the base fabric, fabric defects such as colored yarns in the white fabric are particularly prominent.

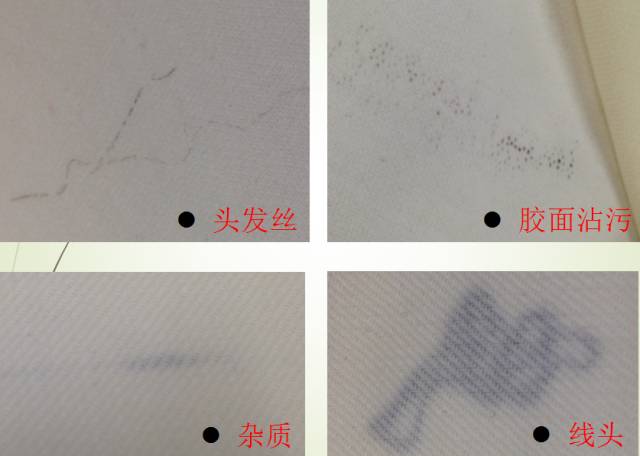
8. Composite entrained foreign matter
Composite glue is easy to process during the PU composite production process Flying in impurities (such as hair, lint and other impurities), the foreign matter entrained when laminating light-colored fabrics will appear on the cloth surface.

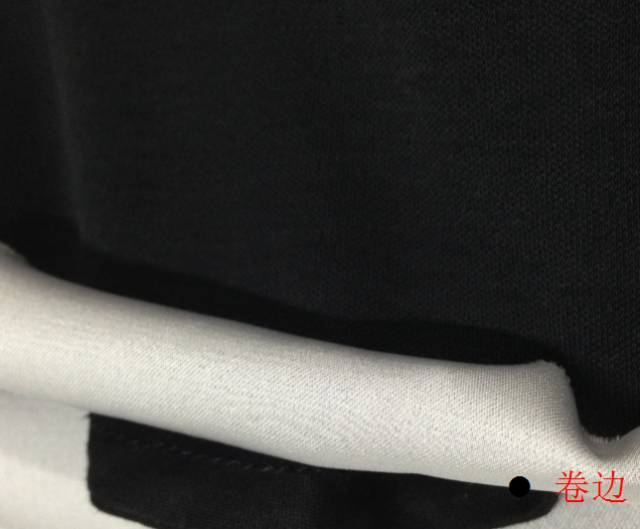
9. Curling
Elastic fabric and non-elastic fabric fit together and The thickness of elastic fabric is thicker than that of non-elastic fabric. If the surface tension of the fabric is not well controlled during the composite production process, it will easily curl.

Summary and measures
Selection of fabric and base fabric
The best: consistent door width, consistent shrinkage, consistent thickness
1. The difference in shrinkage is greater than 3 Above the point, the fabric with a small shrinkage should be thicker than the fabric with a large shrinkage (determined by the specific sample).
2. The fabric before lamination should not be subjected to hydrophobic softening treatment, especially fluorine-containing waterproofing treatment.
3. Try to avoid choosing white fabrics, especially white woolen fabrics, for lamination
4. High-value fabrics have narrower widths than low-value fabrics, and the difference in width cannot exceed 10CM. , otherwise the waste will be greater.
5. Try not to use fabrics with production risks for lamination.
Composite process
1. For fabrics that require dry cleaning, PUR should be selected for lamination. Craftsmanship.
2. When laminating, the fabrics should be aligned with the silk strands to avoid skewed wefts, twisting of straight yarns, etc.
3. Sufficient maintenance treatment in the mid-term, otherwise the peeling strength will be poor.
4. Composite processing seems simple, but it has a lot to do with the experience, technology, and operational proficiency of the composite factory.
5. The composite fabric cannot be recombined. Even if it is peeled off, it will affect the yarn of the fabric, make it hard to the touch, and the yarn is easily punctured by needles.
6. Non-elastic high-density woven fabrics need to be compounded with film, otherwise the fastness will be poor
Composite order process

1. Composite production must go through evaluation-sample-testing before confirmation
2. It is necessary to cut pieces in advance and laminate large goods to fabric lamination. It can only be determined after a fabric sample evaluation
3. The national standard for composite fabrics is only FZ/T 72016-2012 “Knitted Composite Clothing Fabrics”, which is applicable to knitted fabrics and other materials processed by bonding composite processes. Clothing fabrics.
4. It is required that it does not come off after being washed 5 times, does not foam, and the peeling strength is qualified






