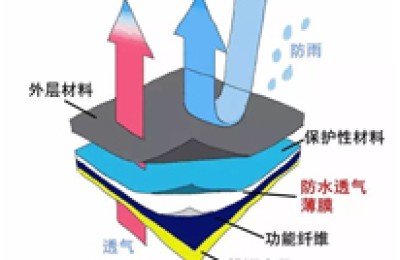
According to reports, according to feedback from cotton trading companies in Qingdao, Nantong, Zhangjiagang and other places, affected by the decline of Zheng cotton oscillation since January 5, the transactions of port pending orders and locked basis RMB resources (including spot and cargo resource RMB quotations) have been relatively Qingdao Port is very busy with customs clearance, warehousing, and company delivery. As the ICE cotton March contract soared to 82 cents/pound, the Zheng cotton CF2405 contract fell below 15,500 yuan/ton, and the sliding tax rate (or 1 % tariff) domestic and foreign cotton prices have narrowed again, and inquiries and shipments of bonded and ship cargo (both quoted for US cotton) are slowing down.
Huaan Futures senior analyst Yao Yu analyzed that as of January 16, the price difference between domestic and foreign cotton under the 1% tariff was 600 yuan/ton, a slight drop from the beginning of the month. The price difference between domestic and foreign cotton narrowed slightly, the market’s enthusiasm for purchasing foreign cotton was not high, and transactions were not strong. The main reason is that the Spring Festival is approaching, the pace of raw material procurement by textile companies has slowed down, the early purchase orders are coming to an end, and downstream companies have begun to take holidays one after another. At present, inquiries and price inquiries for Brazilian cotton and Australian cotton are acceptable, and the transaction volume is slightly better than other varieties.
“The recent contraction in the price difference between domestic and foreign cotton is due to two reasons: on the one hand, domestic cotton prices have declined; on the other hand, overseas orders have recovered. Judging from the start-up of the textile industry in Southeast Asia, the start-up rates of India, Vietnam and other countries have rebounded month-on-month, driving foreign Cotton demand supports external prices.” Wu Xinyang, cotton analyst at CITIC Futures, analyzed that theoretically, as the price difference between domestic and foreign cotton narrows, domestic willingness to import foreign cotton will decrease, but the current price difference has narrowed. It is relatively small, and there is a time lag in customs clearance of cotton imports. It may be difficult to see the impact of reduced import willingness at present.
Gao Feitang, senior cotton analyst at Zhuochuang Information, believes that for downstream textile companies, the narrowing of price differences means that the cost-effectiveness advantage of foreign cotton has declined. During the procurement of raw materials, unless companies purchase foreign cotton specifically due to order demand, most companies will focus on cost-effectiveness. Appropriately increase the proportion of domestic cotton. For upstream ginning companies, the cost of a large amount of Xinjiang cotton this year is relatively high and there is a lack of opportunities to enter the market. However, the narrowing of the price difference between domestic and foreign prices will help change this dilemma. Of course, some cotton import quotas last year will expire, which will also affect the ratio selection of textile companies during the procurement of raw materials.
A cotton company in Changzhou, Jiangsu Province said that after nearly half a month of concentrated sales and destocking, the inventory and cash flow pressure of some cotton traders have been relieved to a certain extent, but most of them are still operating at a loss. It is worth noting that the amount of U.S. cotton shipped in December 2023 and January, February, and March 2024 is relatively large (as of early January, my country has signed a total of 816,300 tons of U.S. cotton for 2023/2024, but only shipped 405,700 tons. tons), coupled with the fact that the sliding tax quota in 2023 is only more than one month away from its validity period, and the delivery of some Brazilian cotton contracts has been delayed due to congestion at the Santos Port and the Red Sea crisis, cotton stocks in China’s main ports may experience a rapid growth before and after the Spring Festival. In the case of growth, once the smoothness of bonded and customs-cleared cotton sales declines and the buyer’s wait-and-see atmosphere heats up, the market will fall into a tug of war again.
From a fundamental perspective, Yao Yu analyzed that the January USDA report showed that global production in 2023/2024 increased by 0.23% month-on-month to 24.642 million tons, consumption decreased by 1.14% month-on-month, reaching 24.479 million tons, and ending stocks increased accordingly. 18.372 million tons. USDA expects China’s production to increase by 108,000 tons to 5.987 million tons, while the consumption view remains unchanged at 7.947 million tons. Ending stocks will increase by 218,000 tons to 8.668 million tons. Currently, the picking of new cotton nationwide has ended, and the processing rate is 97.4%, but the sales rate is only 23.9%, which is 11.6 percentage points lower than the average of the past four years.
Yao Yu said that the 2401 contract has entered the delivery period, with a total of nearly 300,000 tons of cotton delivered. This also reflects that the market supply is sufficient, but spot sales are difficult, and some sales pressure is relieved through futures delivery. At the same time, as the price rebounded in the early stage, the suppressive effect of hedging on the market price gradually appeared. At present, due to the downstream replenishment phenomenon caused by the front-loading of orders, the rebound momentum of this round of cotton prices has weakened. However, the spring and summer orders are difficult to falsify, and the market remains to be seen, so the price downward space is also limited. It is difficult for the market to find a new price release point before the Spring Festival. It is expected that the market will still oscillate within a narrow range. Investors are not recommended to blindly test long prices.
Gao Feitang believes that domestic and foreign cotton prices may still have room for a slight increase in 2024. From a macro market perspective, expectations for the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates may continue to grow, and the relief of pressure on commodities from high interest rates may improve over time. In 2023, domestic market consumption will be significantly stronger than abroad. In 2024, foreign market consumption may recover, and overall consumption will show an improvement trend in the medium and long term. Especially since December last year, domestic yarn inventories have fallen from high levels, and the mentality of market participants has improved significantly. From the supply side, there is not much room for adjustment in foreign production in 2024. Domestic cotton production may be limited due to the increase in the proportion of food crop planting in Xinjiang, which will provide certain support for prices. Therefore, domestic cotton prices are more likely to fluctuate significantly during the planting and harvesting periods. Of course, judging from the current relatively mid-to-high valuations, as well as international market turmoil, uncertain geopolitical situation and changes in the off-peak and peak seasons, the trend of cotton prices in 2024 is not as obvious as that in 2023.
From the current market operation�Looking at the situation, transactions in high-count yarn products are tight, corresponding to strong demand for high-grade, high-quality cotton. Therefore, high-grade US cotton and high-quality Xinjiang cotton will be favored by market participants before the holiday. In addition, the current market is mainly suppressed by downstream yarn inventory. It is expected that as the inventory is consumed, the market in Yuanyue will have greater room for rebound.
Wu Xinyang said that global cotton will continue to accumulate stocks in 2023/2024. Although compared with 2022/2023, there are marginal benefits in terms of output and consumption estimates, but the state of production and sales surplus continues. Judging from the domestic supply and demand situation, the current output is basically on the ground, and the later variables will mainly be on the consumer side of cotton. From the perspective of direct consumption, with the substantial destocking of cotton yarn, the confidence of spinning mills to continue to expand the operation rate in the later period has increased. In addition, Xinjiang cotton yarn production capacity continues to be put into operation, and the possibility of maintaining high-load operation is greater, and the cotton replenishment market is expected to be strong. . From the perspective of terminal consumption, the U.S. apparel fabric market is likely to start a replenishment cycle in 2024, which is expected to promote the placement of orders. Although the positive foreign trade orders are first reflected in Southeast Asian production capacity, they may still spill over to the country. Therefore, domestic cotton consumption is expected to reach last year’s level, maintaining a gap in production and sales. The domestic production and sales gap is mainly made up by imported and reserved cotton. At present, the reserve cotton inventory is low, and the demand for foreign cotton procurement to replenish the inventory is expanding. Taken together, the domestic production and sales gap is expected to promote the formation of price differences between domestic and foreign cotton, giving profits to foreign cotton imports.
</p