Transfer printing is an environmentally friendly and energy-saving new printing technology. There are two main methods: thermal transfer and cold transfer printing. Thermal transfer process is relatively mature and is mostly used for transfer printing of disperse dyes on synthetic fabrics. Fine patterns can be printed on thin polyester fabrics. Cold transfer printing has been a hot research topic in printing technology in recent years. By improving equipment and processes, it can be achieved Realistic printing effects that ordinary printing equipment cannot achieve.

The cold transfer printing machine has a small tension and is suitable for printing fabrics that are easily deformed under tension, such as cotton knitted fabrics. high productivity. Especially for ultra-thin silk, nylon and other fabrics, better transfer effects can be obtained. Compared with traditional printing, the usage of cold transfer printing paste is greatly reduced, which reduces the Water washing pressure. If the cold stack is used to fix the color, the steam consumption can be reduced, and the floating color in water washing can be reduced, thereby reducing the discharge of colored sewage.
Fabric cold transfer printing
Cellulose fiber fabric printing
Generally, cold transfer printing is rarely used on pure cotton woven fabrics, and only particularly fine patterns are used. When ordinary printing equipment cannot achieve the printing effect, transfer printing can be chosen. But transfer printing requires two processes of printing and transfer, the printing effect of the pattern, the fabric The moisture content and transfer rate of pretreatment will have an impact on the printing effect.
The structure of pure cotton knitted fabric is relatively loose, and the fabric is easily deformed under tension. Flat screen printing can be used, but the disadvantage is slow speed and low production efficiency. The use of reactive dye cold transfer printing can print fine patterns such as moire and gradient effects. The printing effect is lifelike and the production efficiency is greatly improved.

Cellulose fiber fabric
Protein fiber fabric printing
Cold transfer printing is also suitable for printing on silk thin fabrics. Silk fabrics are often printed on a platen. Because the fabric is thin, the flat platen is easy to drift. Before printing, silk pulp needs to be applied to the reverse side of the fabric. However, due to the low pulp absorption rate of silk, the printed pattern is easy to bleed. The pattern outline is blurred and unclear, and the production efficiency is low. In recent years, cold transfer printing of acid dyes on silk fabrics has been developed, which has greatly improved the printing effect. It can transfer very realistic and clear photo-realistic effect patterns.
Synthetic fabric printing
nylon thin fabric transfer printing, suitable for winter down jackets and summer skin clothing, which is windproof and sunproof , and in line with young people’s pursuit of fashion. Ultra-thin nylon fabrictyle=”color: #333333; –tt-darkmode-color: #333333;”>Cold transfer printing ink
Imported cold transfer printing ink has stable quality and relatively high price. In recent years, the printing quality and stability of domestic inks have been greatly improved. Cold transfer printing ink types are mainly soluble reactive dyes and acid dye water-based inks, as well as matching diluents. The rheology of water-based ink and oil-based ink are different, and the clarity of printed contours is also different. The lifting rate of water-based ink is not as high as that of oil-based ink, and there are certain limitations in printing deep and dense colors. The viscosity of the ink has a certain impact on the printing effect. The viscosity of the color paste is too low, and the fluidity is good, and the ink is sufficient. However, the pattern is prone to flowing, and it is not suitable for fine lines and large areas of floor-to-ceiling color.

Printing ink
Printing of transfer printing paper
Before printing transfer printing paper, the pattern needs to go through computer color separation, engraving and plate making and other processes. Fine platemaking technology is a prerequisite for obtaining clear layers and realistic patterns. This requires technicians to analyze incoming samples and accurately grasp the thickness of lines and the depth of engraving.
Use a gravure printing machine to print transfer printing paper, reasonably arrange the order of color ink, accurately register the pattern, adjust the left, middle and right pressure to prevent transfer Paper wrinkles, breaks, and color differences. The printing width of the transfer printing paper is 1 to 2cm wider than the fabric. Repeated lofting will produce the best printing effect. Only after the color and light are accurate can the machine be started normally and mass produced.
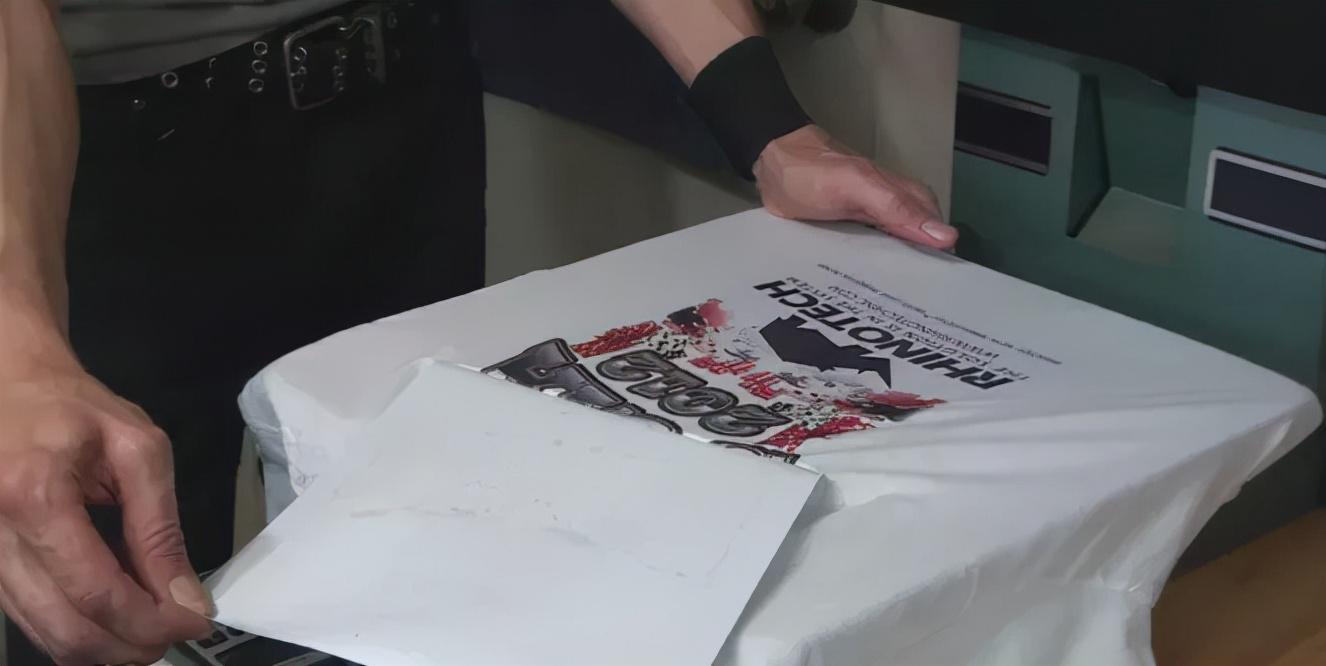

Fabric Laminate to transfer paper and pressurize for transfer
Attach the pretreated moist fabric and transfer paper When combined, the blanket brings the printing paper and fabric into the transfer roller. The fabric and transfer paper will be pressed multiple times when entering the transfer area. Adjust the pressure of each roller according to the printing effect of the pattern and the humidity of the fabric to ensure uniform pressure on the left, middle and right sides of the transfer. Adjust the speed and tension, control the overfeed rate, keep the fabric and transfer printing paper smooth and smooth, and prevent wrinkles on the fabric or transfer printing paper.
Fixed color method
Cold transfer printed fabrics can use different color fixing methods depending on the process and equipment. . If the color is cold stacked after transfer, because the fabric contains moisture, it must be lined with plastic paper to isolate and roll to prevent color matching. Wrap the cloth roll with film paper to strengthen the rotation of the cloth roll pile to prevent uneven coloring , produces dark and light color files. Cold stack fixation is difficult to solve the problem of dye migration. The pattern is easy to bleed, the lines are not fine, the stacking time is long, and the production efficiency is low.
If saturated steam is used to fix the color after drying, control the temperature, humidity and steaming time of the steamer to prevent bleeding and water stains and ensure color development Evenly, adjust the tension to prevent excessive tension, fabric wrinkles and color matching. Drying and baking can also be used to fix the color, but the color development under dry heat conditions is not as good as that in steam. The evaporated color is bright and plump, and the amount of color obtained is also low.

Dye fixing agent
Post-processing
It is best to use open-width washing after transfer printing. Pure cotton fabrics need to be washed with cold running water. For deep and dense colors, anti-stain agents should be added to prevent the white background from being stained, and then soaped at high temperature and washed thoroughly. Only by removing the floating color can we obtain higher color fastness. For silk or nylon fabrics, because acid dyes have a greater affinity for silk and nylon fabrics, they are prone to staining on the white background. Not only must they be fully washed to prevent staining, but they must also be treated with color fixation.
A3;”>Drying and baking can also be used to fix the color, but the hair color under dry heat conditions is not as bright and full as the evaporation color, and the color yield is also lower. p>

Dye-fixing agent
Post-processing
It is best to use flat water after transfer printing. For web washing, pure cotton fabrics need to be washed with cold running water. For deep and dense colors, anti-staining agents should be added to prevent white background from being stained. Then high-temperature soaping should be used to fully wash away floating colors to obtain higher color fastness. For silk or nylon fabrics, because acid dyes have a greater affinity for silk and nylon fabrics, they are prone to whitening. If the bottom is stained, it not only needs to be washed thoroughly to prevent staining, but also needs to be fixed.