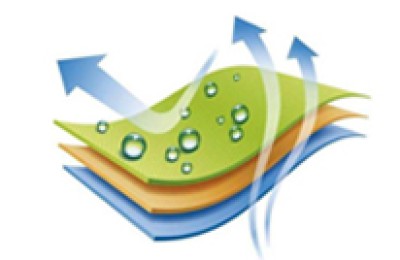
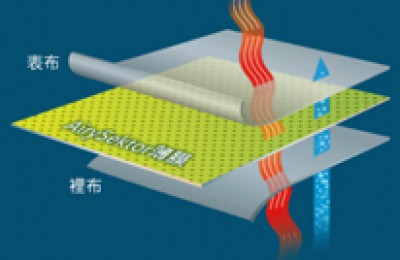
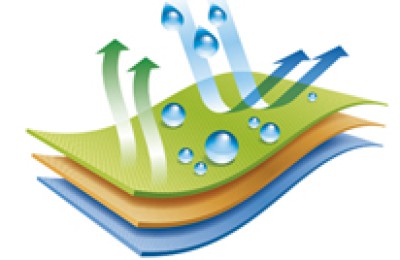
There are two ways for Oxford cloth to have flame retardant properties. Generally, flame retardant fabrics are divided into two types: fiber flame retardant and post-finishing flame retardant. Due to the cost issues of fiber flame retardant and post-finishing flame retardant, currently domestic use There are many flame-retardant finishes, and the flame-retardant fibers are represented by acrylonitrile fiber and aramid fiber.

First The first is to add flame retardant with flame retardant function to the fiber through polymer polymerization, blending, copolymerization, composite spinning, grafting modification, etc., to make the fiber flame retardant. The second is to use post-finishing methods to coat the flame retardant on the surface of the fabric or penetrate into the interior of the fabric. These two methods have different steps in giving fabrics flame retardancy, and the effects they produce are also different.
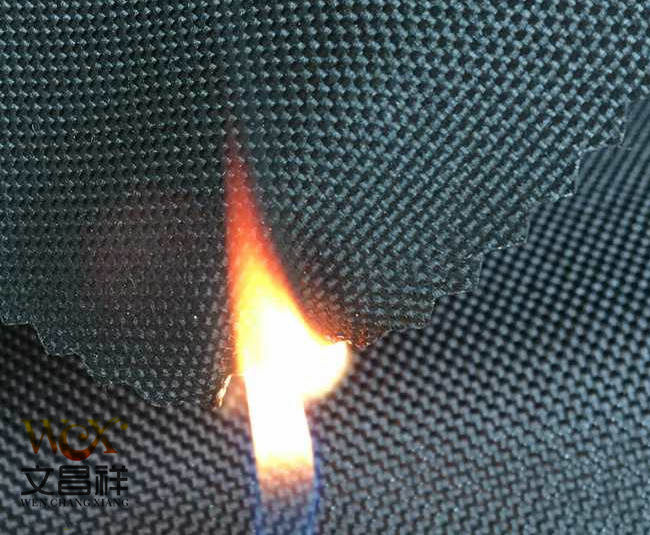

At present, the best way is to modify textiles with nanomaterials and nanotechnology, which is low-cost and has lasting effects. The softness and feel of the textiles have not changed at all, reaching the world’s first-class level. Generally speaking, fiber flame retardant can make full use of flame retardants than fabric flame retardant, and its effect is more durable and softer to the touch. However, in practical applications, multiple flame retardants are often used to achieve flame retardant effects in two or more ways.
Oxford cloth specifications: 1680D, 1200D, 900D, 600D, 420D, 300D, 210D, 150D, etc.
Oxford cloth functional classification: flame retardant Oxford cloth, waterproof Oxford cloth, PVC Oxford cloth, PU Oxford cloth, camouflage Oxford cloth, fluorescent Oxford cloth, printed Oxford cloth, composite Oxford cloth, etc.
</p