Mercerized cotton is the best among cottons. The fabric is made of cotton as raw material, which is made into high-woven yarn through worsted spinning, and then goes through special processing procedures such as singeing and mercerization to make it into a high-quality product that is smooth, bright, soft and wrinkle-resistant. Mercerized yarn. The high-quality knitted fabrics made from this raw material not only completely retain the excellent natural characteristics of raw cotton, but also have a silky luster and a soft fabric feel.
1
Mercerized cotton & pure cotton
Cotton fiber products have long been loved by people because of their good Western-style performance, soft hand feel and comfortable touch when in contact with the human body. However, unprocessed cotton fabrics are prone to shrinkage, wrinkles, and poor dyeing effects, so a large number of cotton fiber products need to be mercerized.

Mercerized The fiber morphological characteristics of cotton fiber have undergone physical changes, the natural twist disappears, the fiber cross section expands, the diameter increases, the cross section is approximately circular, and the regular reflection of light is increased, making the surface of cotton fiber products appear silky. The luster is bright; and due to the tight arrangement of molecules, the strength is higher than that of non-mercerized yarn, which improves the strength of cotton fiber and the adsorption capacity of dyes.
The difference between mercerized cotton and pure cotton
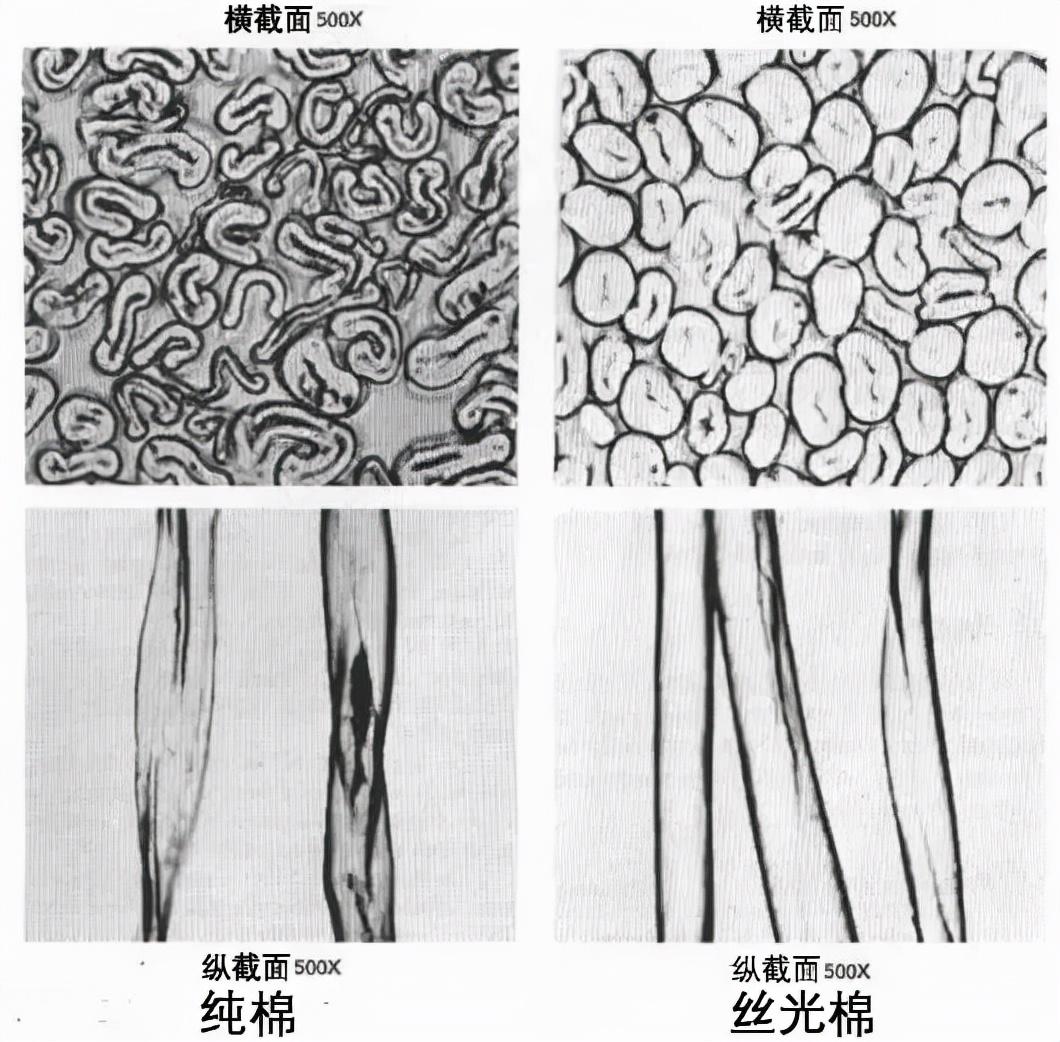
Structural performance
① Pure cotton horizontal The cross-section is round in shape, and the cross-section of mercerized cotton is round.
② The longitudinal section of pure cotton has natural distortion, and the surface wrinkles of mercerized cotton disappear and become smooth.
Physical properties
① Mercerized cotton gloss ratio Pure cotton is better (the surface is smooth after mercerization, and there is less diffuse reflection of light);
② Mercerized cotton is stronger than pure cotton (natural distortion disappears , the fibers are closely arranged and the cohesion force is increased);
③ The dimensional stability of mercerized cotton is higher than that of pure cotton (cellulose molecules are rearranged, and the original inner stress relief).
Chemical Properties
① Mercerized cotton reactivity Improvement (the amorphous region increases, and the hydroxyl group changes from inaccessible to accessible with the rotation of the main valence bond);
② Mercerized cotton is resistant to water, iodine, The adsorption capacity of barium hydroxide and dye is larger than that of pure cotton.
2
Properties of mercerized cotton

1
morphological structure
Fiber diameter increases Becoming round, the longitudinal natural twist rate changes (80% → 14.5%), the cross section changes from kidney to oval, or even circular, and the cell cavity shrinks to a point.
If appropriate tension is applied, the roundness of the fiber increases, the original wrinkles on the surface disappear, the surface smoothness and optical properties are improved. Improvement, increasing the intensity of reflected light, the fabric shows a silky luster.
Changes in fiber morphology within the fabric are the main cause of gloss, and tension is the main factor in improving gloss.
2
Microstructure
Crystallinity ↓ (70% → 50%), amorphous area ↑, making the hydroxyl groups that were originally inaccessible in water become accessible And, therefore, the dye adsorption performance and chemical reaction performance of the fiber are improved;
Since the fiber morphology changes after mercerization, the light scattering on the surface and inside is reduced, so when dyeing with the same concentration of dyes, the dyeing depth also increases.
After the fiber swells, the hydrogen between macromolecules The bonds are broken up, and under the action of tension, the arrangement of macromolecules tends to be neat, which improves the degree of orientation;
Uneven deformation on the fiber surface is eliminated, reducing weak links. The fibers can evenly share external forces, thus reducing breakage caused by stress concentration. In addition, the fibers after puffing and rearrangement are in close contact with each other and the cohesion force also reduces the factors causing breakage due to the slippage of macromolecules.
3
Changes in molecular structure
After cotton fibers swell in concentrated alkali solution, the hydrogen bonds between macromolecular chains are broken up, relaxing the fabric Through stretching, the internal stress stored in the macromolecules is oriented and arranged, and new molecular bonds are established at new positions, and the intermolecular force is greater than before swelling. Finally, under tension, the hydrogen bonds between the aligned fibers are fixed. At this time, the fibers are in a lower energy state and are therefore dimensionally stable.
3
Characteristics of mercerized cotton
Due to fiber After expansion, the fibers are arranged more orderly and the reflection of light is more regular. This enhances gloss.
After mercerization treatment, the crystal area of the fiber Decrease, the amorphous area increases, and the effects of fuel and other chemicals on the fiber occur in the amorphous area, so the dye uptake rate and the chemical reaction performance of the fiber after mercerization are improved.
During the mercerizing process, the fiber macromolecules The arrangement tends to be neat, the degree of orientation is improved, and the uneven deformation on the fiber surface is eliminated, reducing weak links. When subjected to external force, more macromolecules can be evenly shared, the primary breaking strength increases, and the fracture elongation decreases.
Mercerization has a shaping effect and can be used to eliminate ropes It can better meet the quality requirements of dyeing and printing semi-finished products. More importantly, after mercerization, the stability of the fabric’s expansion and deformation has been greatly improved, and the shrinkage rate of the fabric has been greatly reduced.
4
Types of mercerized cotton
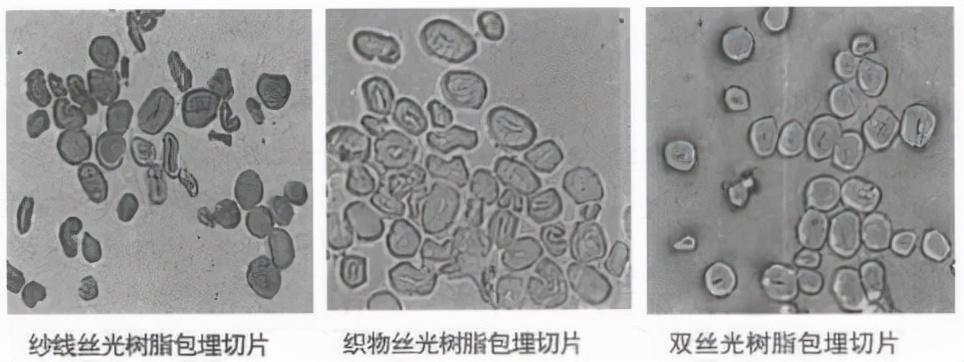
According to different mercerization objectsMercerized cotton can generally be divided into yarn mercerization, fabric mercerization and double mercerization. Silky.
Double mercerized It refers to the fabric made from mercerized cotton yarn.
Yarn mercerization:Refers to a special type of cotton yarn that has been treated with high-concentration caustic soda or liquid ammonia under tension, so that it has both the original characteristics of cotton and a silk-like luster.
Fabric mercerization: Refers to cotton fabrics that have been treated with high-concentration caustic soda or liquid ammonia under tension, making the fabrics glossier, stiffer, and better in shape retention.
According to two mercerization processes, mercerized cotton can refer to cotton yarn that has been treated by yarn mercerization process Threads can also refer to cotton fabrics that have been mercerized.
As it increases, the fracture elongation decreases.
Mercerization has a shaping effect and can be used to eliminate ropes It can better meet the quality requirements of dyeing and printing semi-finished products. More importantly, after mercerization, the stability of the fabric’s expansion and deformation has been greatly improved, and the shrinkage rate of the fabric has been greatly reduced.
4
Types of mercerized cotton
According to different mercerization objectsMercerized cotton can generally be divided into yarn mercerization, fabric mercerization and double mercerization. Silky.
Double mercerized It refers to the fabric made from mercerized cotton yarn.
Yarn mercerization:Refers to a special type of cotton yarn that has been treated with high-concentration caustic soda or liquid ammonia under tension, so that it has both the original characteristics of cotton and a silk-like luster.
Fabric mercerization: Refers to cotton fabrics that have been treated with high-concentration caustic soda or liquid ammonia under tension, making the fabrics glossier, stiffer, and better in shape retention.
According to two mercerization processes, mercerized cotton can refer to cotton yarn that has been treated by yarn mercerization process Threads can also refer to cotton fabrics that have been mercerized.